Understanding the Differences: Isolated vs Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters
DC-DC converters are essential components in modern electronics, playing a crucial role in devices ranging from tractors to golf carts. They are responsible for converting direct current (DC) from one voltage level to another.
Basic Concepts
A DC-DC converter is an electronic circuit that changes a source of direct current from one voltage level to another. It is a type of power converter and is used in power management to provide the desired voltage by increasing or decreasing the current level. Key components include inductors, capacitors, diodes, and switches, which work together to ensure efficient power conversion.
What are Isolated DC-DC Converters?
Isolated DC-DC converters feature a physical barrier, typically a transformer, between the input and output. This isolation ensures that there is no direct electrical connection, offering protection against electric shocks, noise, and ground loop issues. Commonly used in medical equipment and industrial applications, these converters are valued for their safety and noise reduction capabilities.
What are Non-Isolated DC-DC Converters?
Non-isolated converters, in contrast, do not separate the input and output electrically. They are smaller, more efficient, and cost-effective compared to isolated converters. They find extensive use in consumer electronics, automotive applications, and where space and budget constraints are significant considerations.
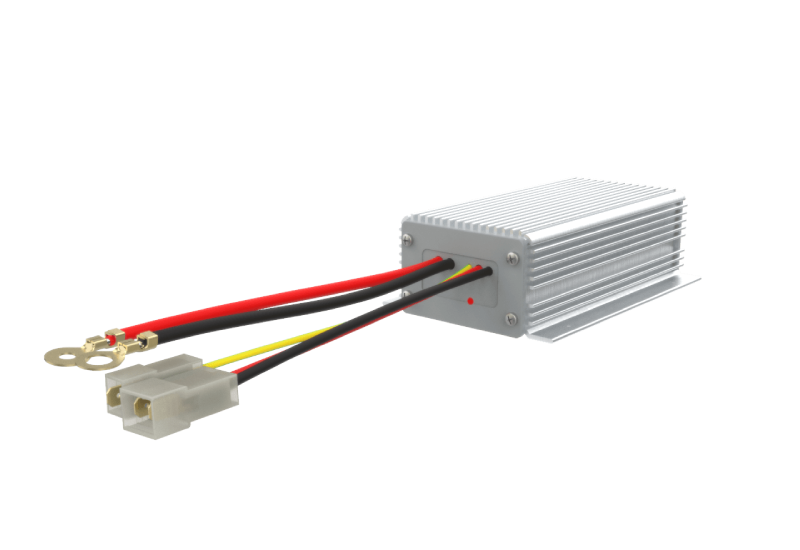 Bestaş Non Isolated DC-DC Converter
Bestaş Non Isolated DC-DC Converter
Comparison of Isolated vs Non-Isolated Converters
- Efficiency: Non-isolated converters generally offer higher efficiency due to fewer components and simpler design.
- Size and Weight: Non-isolated converters are more compact and lighter.
- Cost: Isolated converters are typically more expensive due to additional components like transformers.
- Safety and Compliance: Isolated converters provide better safety, making them suitable for sensitive applications.
- Application Suitability: The choice depends on the application's safety requirements, size constraints, and power efficiency needs.
Choosing the Right Converter for Your Needs
Selecting the right DC-DC converter depends on factors such as the required isolation, efficiency, size, cost, and application environment. For example, for medical and industrial applications where safety and isolation are paramount, an isolated converter is the best choice. Conversely, for consumer electronics, where efficiency and cost are more critical, a non-isolated converter is more suitable.
Recent Advances and Future Trends
The field of DC-DC converters is continuously evolving, with recent advances focusing on improving efficiency, reducing size, and increasing power density. Future trends include the development of converters with better thermal management, higher power capacities, and more intelligent control features, catering to the growing demands of advanced electronic systems.
Conclusion
The choice between isolated and non-isolated DC-DC converters is a crucial aspect of electronic design, impacting the efficiency, cost, and safety of the device. Understanding the differences and applications of each type helps in making informed decisions, ensuring the longevity and reliability of electronic systems.






