Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the transportation landscape, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. However, a critical factor in the widespread adoption of EVs is the availability of robust and efficient charging infrastructure. Understanding the different charging modes is essential for both EV owners and stakeholders to make informed decisions. In this blog, we explore the four primary EV charging modes and their applications, benefits, and limitations.
What Are EV Charging Modes?
Charging modes refer to the methods and levels of communication and power transfer between an EV and the charging infrastructure. They determine how the EV interacts with the power source, ensuring safety, efficiency, and compatibility. The modes are divided into two main types based on the current used:
- AC (Alternating Current): Common in residential and slower charging setups.
- DC (Direct Current): Used for fast-charging stations, providing quicker charging speeds.
Understanding these modes is crucial for optimizing charging performance and ensuring safety.
Overview of the Four EV Charging Modes
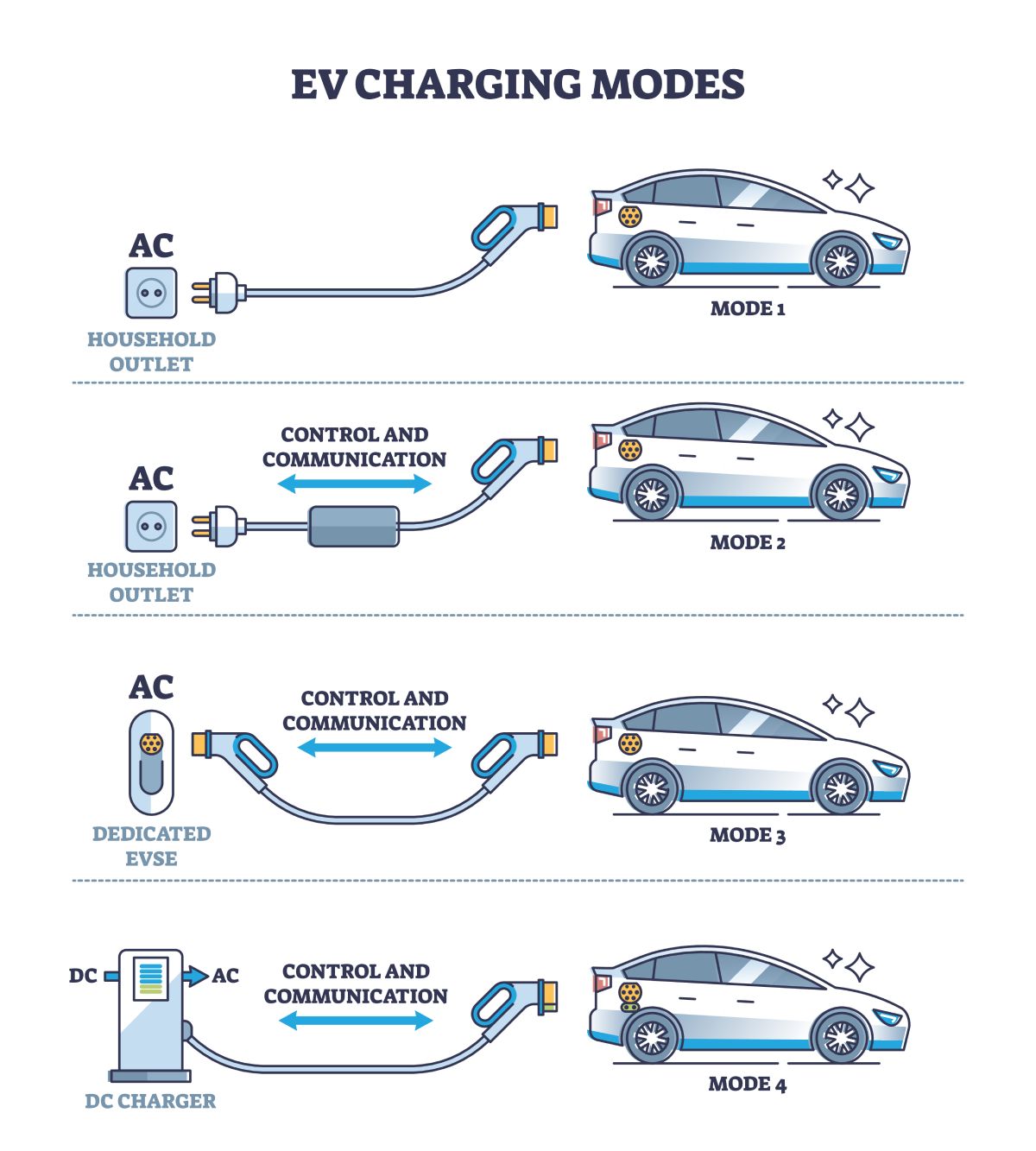
Mode 1: Basic Charging (Prohibited in Many Regions)
- Description: Involves plugging an EV directly into a standard household socket using a simple extension cord.
- Limitations: Lacks safety features like communication between the EV and the power source, leaving users vulnerable to electrical hazards.
- Applications: Rarely used and prohibited in regions like Brussels for safety concerns.
- Key Takeaway: Mode 1 is outdated and discouraged due to its lack of safety and efficiency.
Mode 2: Portable AC Charging
- Description: Uses a special cable with integrated shock protection for AC and DC currents. The cable is often provided with the EV.
- Features:
- Portable and convenient for at-home or on-the-go charging.
- Offers improved safety over Mode 1 with protective mechanisms.
- Applications: Common for domestic charging but limited by slower power output.
- Pros & Cons:
- Pros: Portable and easy to use.
- Cons: Longer charging times compared to higher modes.
Mode 3: AC Charging Stations
- Description: Utilizes dedicated wall boxes or charging stations that are hardwired to the building’s power supply.
- Features:
- Supports smart charging with real-time communication between the EV and the station.
- Offers significantly higher power output compared to Modes 1 and 2.
- Applications: Ideal for residential, commercial, and public charging setups.
- Benefits: Safer and faster charging, making it the preferred option for regular use.
Mode 4: DC Fast Charging
- Description: Directly delivers DC power to the EV battery, bypassing the onboard charger.
- Features:
- Requires specialized infrastructure and connectors.
- High power output ranging from 5 kW to over 400 kW.
- Applications: Found in public charging stations along highways and urban centers.
- Benefits:
- Charges up to 80% of the battery in less than 30 minutes.
- Suitable for long-distance travel and emergency charging.
Comparing Charging Modes
Charging modes differ significantly in terms of power output, safety, and application. Here’s a quick comparison:
| Mode | Current Type | Power Output | Application | Charging Speed |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Mode 1 |
AC | Low (Standard Socket) |
Basic home use (Prohibited in many areas) |
Slow |
|
Mode 2 |
AC | Medium (~10–16 A) | Portable charging for homes |
Moderate |
|
Mode 3 |
AC | High (22 kW) | Dedicated stations (public/private) |
Faster |
|
Mode 4 |
DC |
Very High (400+ kW) |
High-speed public charging |
Faster |
Emerging Trends in EV Charging
Wireless Charging Technologies
- Inductive Charging: Uses magnetic fields to transfer energy without cables. Potential for in-motion charging on electrified roads but costly for widespread implementation.
- Pantograph Charging: Uses overhead catenary lines, commonly for buses, allowing for automated charging while stationary or in motion.
Advances in DC Fast Charging
- New standards offer ultra-fast charging up to 400 kW.
- Challenges include upgrading grid infrastructure and ensuring grid stability to meet increased power demands.
Practical Advice for EV Owners
- Choosing the Right Mode:
- Use Mode 2 for basic home charging.
- Install Mode 3 wall boxes for faster, more efficient charging.
- Rely on Mode 4 for long-distance travel or public fast charging.
- Consider Vehicle Compatibility: Ensure your EV’s charging capacity matches the station’s output.
- Plan Ahead: Identify nearby charging stations and understand their available modes.
Conclusion
The four EV charging modes offer a range of options to suit different needs, from basic home setups to high-speed public charging. Mode 3 remains the most versatile for regular use, while Mode 4 is essential for rapid charging on the go. As the EV industry continues to evolve, advancements in charging infrastructure will play a pivotal role in supporting sustainable transportation. Choose the right charging mode for your needs and embrace the future of electric mobility.















