The automotive industry is experiencing a rapid technological transformation, where advanced communication systems play a crucial role in enabling modern vehicle functionalities. Automotive communication protocols are the unsung heroes of this revolution, facilitating seamless interactions between various systems and components within a vehicle. From ensuring safety-critical operations to powering entertainment systems, these protocols are integral to modern automotive design. In this blog, we will explore the significance of these protocols, their types, and how they are shaping the future of mobility.
What Are Automotive Communication Protocols?
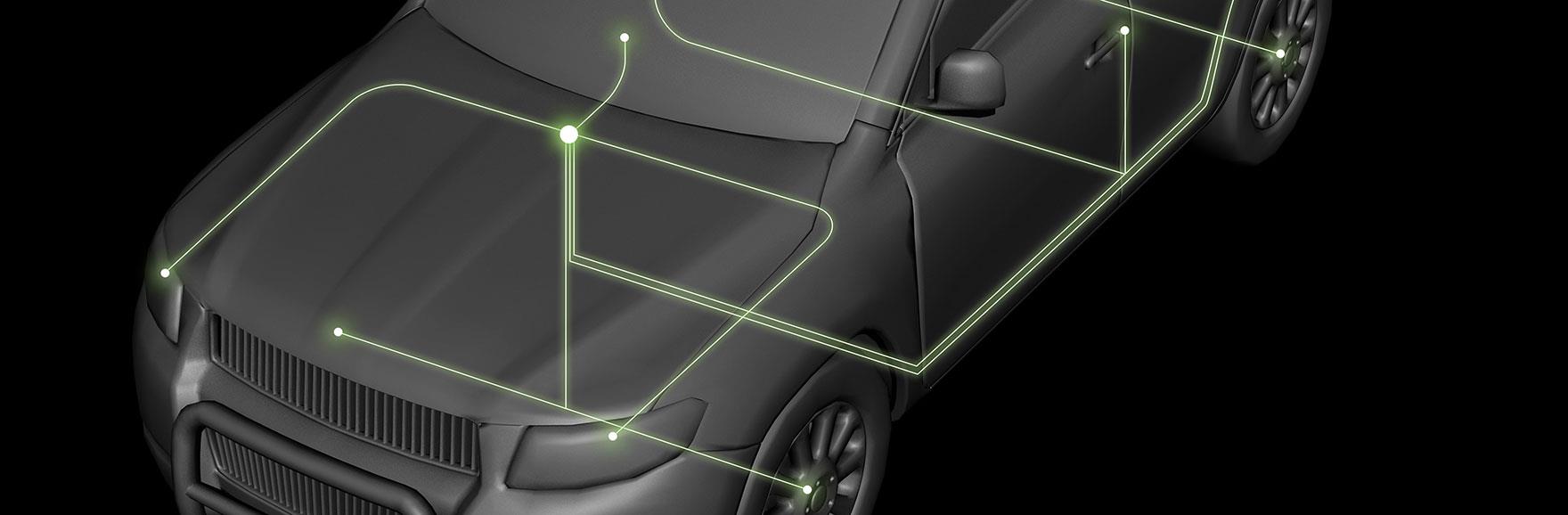
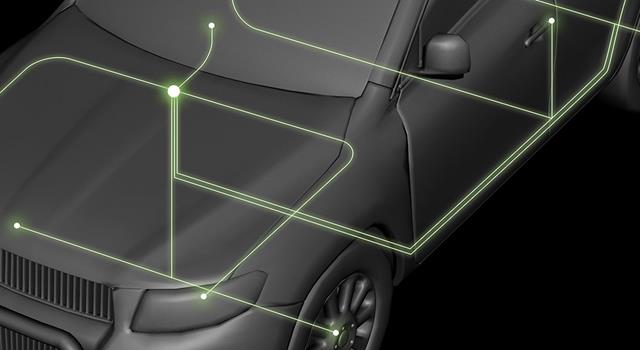
Automotive communication protocols are standardized frameworks that allow different vehicle systems, such as sensors, actuators, and electronic control units (ECUs), to communicate efficiently. These protocols provide a unified language for data exchange, ensuring that all systems work harmoniously to deliver optimal vehicle performance. Beyond functionality, they play a vital role in improving reliability and safety, making them the backbone of modern vehicles.
Why Are Protocols Essential in Modern Vehicles?
Modern vehicles are complex machines with multiple interconnected systems. Automotive protocols are essential for:
- Standardization: Ensuring compatibility and seamless integration across different systems and manufacturers.
- Efficiency: Reducing the complexity of wiring and optimizing system resources.
- Safety: Facilitating real-time communication between safety-critical systems like airbags and ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems).
- Scalability: Supporting the growing needs of connected and autonomous vehicles, which require advanced data handling.
Types of Automotive Communication Protocols
Here are the most commonly used automotive protocols and their applications:
Controller Area Network (CAN):
CAN is the most widely used protocol in the automotive industry. It is robust and facilitates communication between critical systems such as the engine control unit (ECU) and transmission control unit (TCU). Its reliability makes it indispensable for vehicle operations.
Local Interconnect Network (LIN):
LIN is a low-cost protocol used for smaller systems like power windows, seat adjustments, and lighting. It ensures cost-effective communication for non-critical systems.
Media Oriented Systems Transport (MOST):
MOST is designed for high-speed data transfer in multimedia systems, such as in-car entertainment and navigation in premium vehicles.
FlexRay:
FlexRay offers high-speed, reliable communication channels for safety-critical systems like ADAS and autonomous vehicle technologies. Its deterministic nature makes it suitable for applications where timing is critical.
Automotive Ethernet:
Based on standard Ethernet, this protocol is scalable and supports high-speed data transfer. It’s ideal for modern connected vehicles requiring large data bandwidths, such as those integrating IoT and advanced telematics.
SENT (Single Edge Nibble Transmission):
SENT is a low-cost protocol for transmitting sensor data, offering a simple solution for analog-to-digital communication in vehicle systems.
DSRC (Dedicated Short-Range Communications):
DSRC enables Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) and Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) communication, essential for real-time traffic management and enhanced road safety.
Key Components of Protocol Stacks
Automotive protocol stacks are structured into layers, each with specific responsibilities:
- Signal Layer: Abstracts the CAN stack, allowing applications to access data without dealing with protocol details.
- Diagnostic Communication Manager (DCM): Handles diagnostic requests, such as reading data or resetting processors.
- PDU Router: Manages data routing between single-frame and multi-frame communication layers.
- CAN State Manager (CAN SM): Controls communication states (No Communication, Silent, Full Communication).
- CAN Network Manager (CAN NM): Coordinates sleep and shutdown operations within the network.
Advantages of Automotive Protocols
The adoption of automotive communication protocols brings several benefits:
- Improved System Integration: Seamless communication between systems enhances vehicle performance.
- Increased Safety: Real-time interaction between safety-critical systems reduces the risk of accidents.
- Enhanced User Experience: Enables advanced entertainment, navigation, and comfort features.
- Interoperability: Ensures compatibility across systems from different manufacturers.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Reduces wiring and simplifies system architecture, lowering production costs.
Future of Automotive Protocols
As vehicles become smarter and more connected, automotive protocols will continue to evolve. Key trends include:
- Support for Autonomous Vehicles: High-speed, reliable protocols like FlexRay and Automotive Ethernet will be pivotal in enabling advanced driverless systems.
- Enhanced Connectivity: Protocols like DSRC and Automotive Ethernet will drive innovations in V2V and V2I communication.
- IoT Integration: Automotive Ethernet’s scalability makes it a perfect fit for integrating IoT devices in connected cars.
Conclusion
Automotive communication protocols are indispensable to modern vehicles, ensuring seamless data exchange between systems for improved performance, safety, and reliability. As the automotive industry continues to innovate, these protocols will play an even more significant role in shaping the future of mobility. From enabling connected cars to supporting autonomous driving, automotive protocols are the foundation for the next generation of transportation.